Mauritius travel vaccine and advise.

*Check if you up to date with some of the routine(childhood) vaccines
Schedule an AppointmentMost people get vaccines
Most US residents get these before traveling to Mauritius
Some people get vaccines
These are recommended for only a few travelers to Mauritius
Rabies
Routine childhood vaccines
These are commonly given to children in the US. Check whether you’re up to date.
Varicella (Chicken Pox)
Tetanus, Diphtheria, and Pertussis (TDaP)
About the vaccine
Hepatitis A immunization schedule
Travelers are recommended to receive two doses of Hepatitis A vaccine, the second dose should be administered 6 to 12 months after the first.
How far in advance should travelers be immunized against Hepatitis A?
Ideally, a traveler should get hepatitis A (HAV) vaccine more than two weeks before departure. However, it will provide some protection even if it is given less than two weeks before departure.
How effective is the vaccine?
A single hepatitis A shot is more than 95% effective. Two doses are almost 100% effective.
How is hepatitis A transmitted?
Hepatitis A is a viral infection that is transmitted through the following:
- contaminated food
- contaminated water
- oral–anal sexual intercourse
Who should get the Hepatitis A vaccine?
The HAV vaccine is recommended for friends and family members of people who have hepatitis A, homosexual men, and international travelers visiting any geographical area except the following:
- Canada
- Western Europe & Scandinavia
- Japan
- New Zealand
- Australia
What If I May Have Already Been Vaccinated against Hepatitis A?
How long does post-vaccination immunity last?
One dose of hepatitis A immunization provides protection for at least 10 years. Two doses provide protection for at least 20 to 25 years.
Should I have my immunity to hepatitis A checked with a blood test if I have been vaccinated?
No. It is not recommended that you have your immunity to hepatitis checked unless your vaccination was not given properly.
I can’t find my records and have no time for a blood test: Is it safe to get an extra injection of hepatitis A vaccine?
Yes. It is medically safe to get an extra (unnecessary) dose of hepatitis A vaccine. Some people choose this option to be on the safe side.
If Immunization is not an option
How serious is Hepatitis A?
Hepatitis A does not usually cause serious long-term health issues, but you might get very sick if you contract it. You will need to see a doctor to be diagnosed properly (mainly to rule out other health conditions). You will recover with supportive treatment and diet. Most people are contagious for two weeks.
Is Hepatitis A curable?
Yes. Most people (99.9%) recover without any long-term residual effects on their health. However, this infection is fatal in 0.3%–0.6% of cases. Supportive treatment consists of the following:
- resting
- eating small portions of food and avoiding greasy food as long as you have hepatitis
- avoiding alcohol until your doctor says it is okay to drink
- taking over-the-counter pain medication (but do not take Tylenol or its generic form, acetaminophen)
- avoiding hot baths
Can hepatitis A be prevented without vaccination?
You can decrease your chances of contracting hepatitis A by doing the following:
- washing your hands with soap (especially before you eat)
- not eating food prepared by someone with hepatitis A
- drinking safe, adequately chlorinated water
- boiling or cooking what you drink and eat for at least one minute at 185 °F
Please note that alcohol-based sanitizing products provide no hepatitis A protection.
Should I purchase travel insurance since I am not vaccinated?
Yes. If you contract hepatitis A, you will probably need to be hospitalized. Medical services outside the United States are not covered by most US health insurance policies. There are various companies that offer travel insurance packages for US travelers. Here are links to some of them:
- WorldMed Insurance
- InterMedical Insurance
- Travel Insurance Select
- World Nomads
- American Visitor Insurance
Be sure to pay attention to and understand policy exclusions and deductible amounts before committing to any insurance plan.
How common is the Hepatitis A in Mauritius?
In Mauritius, about 81.6% of population are immune to hepatitis A infection. This means that around 81.6% of people have ever been exposed to the virus.
How soon after exposure to hepatitis A do symptoms develop?
The incubation period (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for hepatitis A is an average of four weeks (the range is 14–50 days). Be aware that you will be contagious for two weeks after you get sick.
What is the likelihood of hospitalization if I contract hepatitis A?
High! If you get hepatitis A you will be very sick, and you won’t know what is causing your illness so you will need to see a doctor to be diagnosed. Various diseases have similar symptoms, and a doctor will need to examine you and possibly conduct some tests to reach a diagnosis and make a treatment plan. In addition, hepatitis A may (very rarely) cause serious health complications. It is highly recommended that you see your doctor if you think that you may have hepatitis A.
About the vaccine
Vaccination schedule for Typhoid
There are two forms of vaccines that protect from typhoid infection: injectable and oral typhoid vaccines. Here are the administration schedules for both types:
| Vaccine type | Dose # | Time of administration |
|---|---|---|
| Injectable | Single dose | At least 2 weeks prior to departure |
| Oral | 4 pills during 7 day period (every other day) | The first pill should be taken at least 10 days prior to departure. The 2nd, 3rd, and 4th doses should be taken every other day. |
Comparison of two Typhoid vaccine types
Several factors should be considered when choosing between the two types of typhoid vaccines. They are summarized below.
| Vaccine Type | Effectiveness | Protection Duration | Side Effects | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injectable | 64-72% | 2 years | Most common
Rare
|
Advantages
|
| Oral | 67-80% | 5 years |
|
Advantages
Disadvantages
|
How is Typhoid transmitted?
Typhoid is a bacterial infection that is mainly transmitted through infected food and/or water.
Who should be vaccinated?
The following groups of people should get typhoid vaccine:
- travelers visiting high-risk geographical areas
- friends and family members of people with typhoid
- laboratory workers who are at risk of typhoid bacteria exposure
How far in advance should travelers be immunized against typhoid?
It is recommended that travelers receive typhoid immunization at least one month before departure. However, it will give some protection if it is administered closer to the departure date.
How effective is the typhoid vaccine?
There are some differences in the effectiveness of the two forms of the typhoid vaccines:
- The oral vaccine is about 67%–80% effective.
- The injectable vaccine is about 64%–72% effective.
What If I May Have Already Received the Typhoid Vaccine?
How long does post-vaccine immunity last?
- Oral vaccine protection lasts five years.
- Injectable vaccine protection lasts two years.
I can’t find my records. Is it safe to get an extra dose?
Yes. An extra dose of the typhoid vaccine is not medically harmful. Some people choose to get an extra dose to be on the safe side.
If Immunization is not an option
How serious is typhoid?
More than 30% of typhoid cases are fatal if untreated. Life-threatening complications of this disease include the following:
- internal bleeding
- gastrointestinal perforation (a hole in the digestive tract)
Is typhoid curable?
Yes. The disease can be cured with antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, cefazolin, and Zithromax.
Can typhoid be prevented without the vaccine?
To avoid contracting typhoid, it is recommended that travelers do the following:
- eat only hot, well-cooked food
- do not drink raw milk
- make sure any milk products are made of pasteurized milk
- avoid water unless it is boiled or bottled
- wash and peel fruits and vegetables
- wash your hands frequently with soap and water
- if you cannot wash your hands, use hand sanitizer that is at least 60% alcohol
Should I get travel insurance since I am not vaccinated?
Yes. If you are not immunized against typhoid and you contract typhoid, you will need to be hospitalized. Medical services outside the United States are not covered by most US health insurance policies. There are various companies that offer travel insurance packages for US travelers. Here are links to some of them:
- WorldMed Insurance
- InterMedical Insurance
- Travel Insurance Select
- World Nomads
- American Visitor Insurance
Be sure to pay attention to and understand policy exclusions and deductible amounts before committing to any insurance plan.
How common is typhoid in the region?
During an 8-year study conducted in Mauritius from 1997 to 2004, only 25 cases of typhoid fever were reported in the country. Of these cases, only 6 were acquired in Mauritius, the rest were reported in Mauritius but were acquired overseas. Mauritius has a population of 1.26 million people.
How soon after exposure to typhoid do symptoms develop?
The period between exposure to typhoid and the development of the first symptoms (the incubation period) is 10–14 days.
What is the likelihood of hospitalization if I contract typhoid?
High! You will be very sick and will not know what is causing your symptoms, so you will need to see a doctor to be diagnosed and treated. Various diseases have similar symptoms, and a doctor needs to examine you and conduct some tests to reach a diagnosis and make a treatment plan. In addition, if untreated, typhoid may result in serious health complications. It is highly recommended that you see your doctor if you think that you may have typhoid.
Who needs a shot?
How effective is the hepatitis B vaccine?
Three dose series of HBV vaccine are about 80%–100% effective. Hepatitis B immunity last for 30 years after the completion of the series of three injections.
Is it necessary to get adult booster doses of the hepatitis B vaccine before traveling?
The immunity lasts for 30 years after the completion of the 3-dose series of Hepatitis B (HBV). One or more adult booster doses of the hepatitis B vaccine is needed only by people who do not have either of the following:
- laboratory evidence of hepatitis B immunity (having been sick or immunized)
- a valid vaccine administration record of having been immunized against hepatitis B
I can’t find my records: what are my options?
Travelers who can’t find their vaccine administration record have two options:
- Ideally, get tested for the presence of hepatitis B immunity.
- If you are running out of time and want to play it safe, you can get an extra vaccination without long-term health consequences. People choose this option when time is the most important factor in the decision-making process.
What should I do if I have a low level of hepatitis B immunity?
If you were vaccinated more than 30 years ago and therefore have an insufficient level of immunity to the hepatitis B virus, you should get a fourth dose (one booster shot) of the vaccine.
If I completed my hepatitis B vaccinations but can’t find my records, is it safe for me to get one extra shot?
Yes. A booster Hepatitis B vaccination will be absolutely safe.
How far in advance should I get a booster dose of the hepatitis B vaccine?
To ensure that the vaccine will provide a sufficient level of immunity, it is recommended that a booster dose of the vaccine be given one to six months before departure. However, if you do not have that much time, you may get the booster vaccination as late as one week before departure. In that case, the booster dose will provide about 20.5% protection.
How should I check my records?
How should I check my immunization records?
You should first check to see whether you received the hepatitis B vaccine, and if so how many doses you received (ideally you received three doses, with the second and third shots having been given one and six months after the first one).
How long does hepatitis B immunity last?
People who have been vaccinated against hepatitis B are immune for up to 30 years.
My records show that I have been vaccinated: should I get tested to make sure that I will be safe?
Usually, getting tested after completing hepatitis B vaccinations is not recommended. However, some people who are at increased risk of contracting hepatitis B (intravenous drug users, healthcare professionals, and sex workers) can get a blood test to be safe.
How can I get my records?
Sadly, there is no nationwide system that maintains vaccine administration records in the United States. However, there are several ways of finding your vaccine administration record:
| Ways to Find Your Vaccine Administration Record | |
|---|---|
|
|
I can’t find my records: what should I know?
It is customary for US pediatricians to offer the hepatitis B vaccine to children. Most people born after 1980 are immune to hepatitis B even though this is not considered a necessary vaccination.
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
Hepatitis B is usually transmitted in one of the following ways:
Incubation period for hepatitis B
The incubation period (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for hepatitis B is one-and-a-half to six months.
What if I get sick as an adult? Is it serious?
These days, most cases of hepatitis B are curable with very effective antiviral medication. However, hepatitis B may lead to serious complications, such as the following:
- cirrhosis (liver scarring)
- liver cancer
- liver failure
- death
How can I minimize my chances of being infected?
If you not sure about your hepatitis B status, you can minimize your risk of contracting hepatitis B by
- practicing protected sex,
- never sharing needles, and
- covering sores and wounds with a waterproof dressing.
About the vaccine
Rabies immunization schedule
International travelers need 3 consecutive rabies jabs, on the following schedule:
- first vaccination (shot): day 0
- second vaccination: 7 days after the first vaccination
- third vaccination: 21 or 28 days after the first vaccination
How far in advance should travelers be immunized against rabies?
The first dose of rabies vaccination should be done at least 28 days before departure so the three-dose schedule can be completed. People who are not able to get three doses of the vaccine should not be vaccinated at all.
How effective is the vaccine?
Pre-exposure rabies vaccination does not completely prevent development of the disease. It is recommended for two reasons:
- People who are vaccinated and then exposed to rabies will not need to receive rabies immune globulin, which should be given on the day of exposure. This fact can be life-saving for people who have traveled to a destination where immune globulin is not readily available. Administration of immune globulin may be delayed for no more than 7 days after exposure.
- People who are vaccinated before exposure will need only two doses of vaccine after an exposure instead of four.
How long does post-vaccination immunity last?
Immunity after rabies vaccination lasts three to five years (for more information click here. However, the following people need a booster dose of the vaccine every six months to two years:
- rabies vaccine production facility employees
- wildlife officers
- veterinarians
- laboratory workers who are exposed to rabies
Making a Decision about Getting Vaccinated
How is Rabies transmitted?
Rabies is transmitted mainly by the bite of an infected animal (dog, cat, monkey, or bat). People may also be infected if they have an open wound that is exposed to the saliva of an infected animal.
What activities increase the risk of contracting rabies?
In general, all activities that increase the chances of contact with an infected animal also increase the risk of getting rabies. Here are some examples:
- outdoor activities such as camping, caving, and biking
- working with animals (being a veterinarian or wildlife professional)
- traveling to a high-risk area
How common is the Rabies in Mauritius?
Mauritius is now considered rabies-free. Since the 1970s, not a single case has been reported in this country.
How serious is Rabies?
Rabies is an extremely serious, deadly disease. People who get it and are not promptly treated will develop symptoms such as the following:
- weakness
- hallucinations
- abnormal behavior
- hydrophobia (fear of water)
Everyone who develops rabies symptoms will die within seven days.
Who needs a shot?
How effective is the MMR vaccine?
- One dose is more than 78% effective.
- Two doses are more than 88% effective.
Two doses usually provide lifelong immunity.
Is it necessary to get adult booster shots?
Most people who have received two doses of the MMR vaccine have lifelong immunity against measles, mumps, and rubella. However, some people need to get additional doses of the vaccine:
- People who got the inactivated measles vaccine between 1963 and 1967 (one or two doses are needed)
- People who are at increased risk of getting mumps (if there is a mumps outbreak in their country) should receive two doses of the vaccine
I can’t find my records: what are my options?
People who can’t find their MMR vaccine administration record have two options:
- Ideally, get tested for the presence of MMR immunity.
- If you are running out of time and want to play it safe, you can get an extra vaccination without it causing long-term health consequences. People choose this option when time is the most important factor in the decision-making process.
What should I do if a blood test shows a low level of MMR immunity?
If you have a low level of MMR immunity, you need to get one MMR vaccination.
If I completed my MMR vaccinations but can’t find my records, is it safe for me to get an extra shot?
Yes. It is not harmful to get an additional vaccination.
How far in advance should travelers be vaccinated against MMR?
Tourists should get one MMR vaccination at least two weeks before traveling. But they should be vaccinated even if there are fewer than two weeks before departure.
How should I check my records?
How should I check my immunization record?
You should first pay attention to the number of doses of the MMR vaccine you’ve received. Ideally, there should be two doses received at least four weeks apart.
My records show that I have been vaccinated: should I get tested to make sure that I’ll be safe?
No. There is no need to get tested or revaccinated.
How can I get my records?
Sadly, there is no nationwide system that maintains vaccine administration records in the United States. However, there are several ways of finding your vaccine administration record:
| Ways to Find Your Vaccine Administration Record | |
|---|---|
|
|
I can’t find my records: what should I know?
More than 89% of children in the United States got at least one dose of the MMR vaccine when they were between 19 and 35 months old. By the beginning of 1980, all US schools required proof of immunization before a child was admitted to a public school. Therefore, even if you can’t find proof of immunization, it is highly likely that you received the MMR vaccine before beginning school.
However, if you want to be 100% sure that you will be safe, you should (ideally) get a blood test to check your MMR immunity level or just get one vaccination before traveling. An extra shot (even if it is unnecessary) will not cause any long-term health issue.
How are measles, mumps, and rubella transmitted?
| Disease | Methods of Transmission |
|---|---|
| Measles and Mumps | |
| Rubella |
|
Incubation period for measles, mumps, and rubella
The incubation periods (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for measles, mumps, and rubella differ slightly:
| Disease | Incubation Period |
|---|---|
| Measles | 10–12 days |
| Mumps | 16–18 days |
| Rubella | 12–23 days |
What if I get sick as an adult? Is it serious?
Measles, mumps, and rubella are dangerous diseases that may have serious, even fatal, consequences. Complications of these infections are summarized below.
| Measles | Mumps | Rubella |
|---|---|---|
|
In newborns born to infected women
|
How can I minimize my chances of being infected?
If you’re not sure about your immunization status and want to know how to prevent measles, mumps, and rubella, it is recommended that you do the following:
- Wash your hands with soap and water
- Use a hand sanitizer if no soap is available
- Avoid touching your face
- Avoid close contact with an infected person (e.g., kissing, hugging, using the same cup)
Who needs a shot?
How effective is the varicella vaccine?
- One dose of the varicella vaccine is about 80% effective
- Two doses of the varicella vaccine are over 92% effective
Vaccinated people will have immunity to chicken pox for about 10–20 years.
A blood test (in 10–20 years) can tell you if you are still immune.
Is it necessary to get adult booster doses of the varicella vaccine before traveling?
Vaccinated people will have immunity to chicken pox for about 10–20 years.
Adults need one or more booster doses of the varicella vaccine only if they do not have
- laboratory evidence of chicken pox immunity (having been immunized or having had chicken pox already) or
- a valid vaccine administration record showing they’ve been vaccinated against varicella.
I can’t find my records: what are my options?
People who can’t find their vaccine administration record have two options:
- Ideally, get tested for the presence of MMR immunity.
- If you are running out of time and want to play it safe, you can get an extra vaccination without it causing long-term health consequences. People choose this option when time is the most important factor in the decision-making process.
What should I do if a blood test shows a low level of varicella immunity?
If you have been vaccinated but you have a low level of immunity, you need to get one vaccination.
If I completed my varicella vaccinations but can’t find my records, is it safe to get one extra shot?
Yes. The extra dose of the vaccine will not be harmful.
How far in advance should travelers get a varicella vaccine booster shot?
Travelers should get a varicella booster shot two to four weeks before departure.
How should I check my records?
How should I check my immunization records?
You should first pay attention to the number of doses of varicella vaccine you have received. Ideally, there should be two doses received at least four weeks apart.
How long does varicella immunity last?
Vaccinated people will have immunity to chicken pox for about 10–20 years. A blood test (in 10–20 years) can tell you if you are still immune.
My records show that I have been vaccinated: should I need to get tested to make sure that I will be safe?
No. People who received two doses of the vaccine (as documented in the vaccine administration record) do not need to receive additional doses or have a blood test.
How can I get my records?
Sadly, there is no nationwide system that maintains vaccine administration records in the United States. However, there are several ways to find your vaccine administration record:
| Ways to Find Your Vaccine Administration Record | |
|---|---|
|
|
I can’t find my records: what should I know?
By the beginning of 1980, all US schools required proof of immunization before admission to a public school. Therefore, even if you do not have proof of immunization, it is highly likely that you received the varicella vaccine before beginning school.
How is varicella transmitted?
Chicken pox (varicella) is an extremely contagious infection. It is mainly transmitted through
- direct contact with someone with chicken pox (touching their rash) or
- being near an infected person who coughs or sneezes.
Incubation period for varicella
The incubation period (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for chicken pox is two to three weeks. For most people, it is 14–16 days.
What if I get sick as an adult? Is it serious?
Yes! Complications of chicken pox may be as serious as death. The following are the most common complications:
- infection of one or more lungs
- brain infection/inflammation
- infections of the bloodstream
- bleeding problems
- dehydration
How can I minimize my chances of being infected?
The varicella vaccine is recognized as the way to prevent chicken pox. But if you do not want to or can’t receive a shot, following the recommendations below may minimize your risk of infection:
- Stay away from infected people
- Wash your hands more frequently
- Maintain proper hygiene
Who needs a shot?
How effective is the tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis vaccine?
The TDaP is about 76%–89% effective.
Is it necessary to get adult booster doses?
Yes! Everyone, including travelers, should get a TDaP booster dose once every 10 years.
I can’t find my records: what are my options?
People who can’t find their vaccine administration records should get one TDaP vaccination and then get a booster shot 10 years later.
If I completed my tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis vaccines but can’t find my records, is it safe for me to get one extra shot?
Yes. It is safe to get an additional dose of TDaP vaccine.
How far in advance should travelers get a TDaP booster vaccination?
Tourists are advised to get a TDaP booster two weeks before departure.
How should I check my records?
How should I check my immunization records?
Look to see how many years have passed since your last TDaP immunization. If it’s been more than 10, you should get a booster dose.
How long does immunity against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis last?
TDaP immunity lasts for 10 years.
How can I get my records?
Sadly, there is no nationwide system that maintains vaccine administration record in the United States. However, there are several ways to find your vaccine administration record:
| Ways to Find Your Vaccine Administration Record | |
|---|---|
|
|
I can’t find my records: what should I know?
It is quite likely that you have been vaccinated against TDaP.
- TDaP is a vaccination that people commonly get every 10 years from primary care physicians during an annual physical exam. US primary care physicians are usually good at making sure people get this particular vaccine.
- People often get this vaccine after any incident involving skin damage: an animal bite, cut, scrape, etc.
- Gynecologists advise relatives to be vaccinated against whooping cough before the birth of a child. Pertussis (whooping cough) is part of the TDaP vaccine.
How are tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis transmitted?
| Disease | Method of Transmission |
|---|---|
| Tetanus |
|
| Diphtheria |
|
| Pertussis |
|
Incubation period for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis
The incubation periods (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis are given below.
| Disease | Incubation Period |
|---|---|
| Tetanus | |
| Diphtheria | |
| Tetanus |
What if I get sick as an adult? Is it serious?
Tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis may result in life-threatening health problems, including disability and death. The table below summarizes the most common complications.
| Tetanus | Diphtheria | Pertussis |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
How can I minimize my chances of being infected?
If you not sure about your TDaP status, you can minimize your risk of contracting tetanus or pertussis (but not diphtheria):
| Disease | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|
| Tetanus |
|
| Diphtheria |
|
| Pertussis |
Who gets it?
The polio vaccine that is given in the United States is about 99% effective and lasts for at least 18 years.
Immunity to polio lasts for at least 18 years after the completion of the initial series. One adult booster dose of the polio vaccine after age 21 is needed only by people who do not have
- a laboratory evidence of polio immunity or
- a valid vaccine administration record.
People who can’t find their vaccine administration record have two options:
- Ideally, get tested for the presence of polio immunity.
- If you are running out of time and want to play it safe, you can get an extra shot without long-term health consequences. People choose this option when time is the most important factor in the decision-making process.
If you have been vaccinated but you have a low level of polio immunity, one additional shot is considered sufficient.
Yes. It is safe to get an additional shot.
Travelers should get a booster shot of polio vaccine at least four weeks before traveling.
Checking my records
You should first check to see how many doses of polio vaccine you have received. Ideally, there should be three doses received at the following times:
- First dose – anytime
- Second dose – 1 or 2 months after the first dose
- Third dose – 6 to 12 months after the second dose
Almost everyone who has received all three doses of the polio vaccine is protected from the disease for at least 18 years.
No. If you have completed the vaccination schedule, there is no need to get your immunity tested.
Finding my records
Sadly, there is no nationwide system that maintains vaccine administration records in the United States. However, there are several ways to find your vaccine administration record:
| Ways to Find Your Vaccine Administration Record | |
|---|---|
|
|
No records found?
By the beginning of 1980, all US schools required proof of immunization before admission to a public school. Therefore, even if you don’t have proof of immunization, it is highly likely that you received the polio vaccine before beginning school.
Polio is spread through the following routes:
- eating contaminated food
- having poor hygiene
The incubation period (the period between being infected and developing the first symptoms) for polio is as follows:
- 3–6 days for the non-paralytic form of the disease
- 7–21 days for the paralytic form of the disease
Sometimes, polio causes very serious health problems. Here are some polio-related complications:
- paralysis (inability to move body parts)
- lung damage
- lung inflammation
- myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle)
If you are not sure about your polio vaccine status, you can minimize the risk of contracting it by doing the following:
- washing your hands with soap and water
- drinking safe water
- eating safe food
Customer
reviews
Medical packing list specific to Mauritius
If you travel to Mauritius, don’t forget to take these items with you:
- medication prescribed by your doctor
- antibiotics (for travelers’ diarrhea)
- malaria prophylaxis medication
- antihistamine (Dimetane, Zyrtec, Tavist, Claritin)
- painkillers
- insect repellent
- altitude sickness medicine
- hand sanitizer
- water purification tablets
- sunscreen (SPF 15 or more)
- aloe gel (in case of sunburns)
- digital thermometer
- 1% hydrocortisone cream
Local health clinics
Hopefully, you will not need to see a doctor while being on vacation in Mauritius. However, in order to ensure your well-being, we have found some travel clinics where you can receive medical care.
| Travel Clinic | City | Address | Phone # | Web page |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dr AG Jeetoo Hospital (Civil) | Port Louis | Volcy Pougnet Street (ex-rue Madame), Port Louis, Mauritius |
+230 203 1001 |
- |
| Clinic Darne | Grand Baie | XHHH+5VQ, Grand Baie, Mauritius | +230 601 2500 |
http://www.fortiscliniquedarne.com |
| Centre De Flacq | Flacq | Royal Road, St.Remy, Next to CEB Flacq, Centre De Flacq | +230-4139173 | https://www.dragarwal.com/eye-hospitals/ |
American embassy and consulates in the most-visited areas
The information on US embassies and consulates in Mauritius may be found on the US embassy of Mauritius and Seychelles.
Insect repellents
Different insect repellents have different active ingredients. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of the most common ones:
| Ingredient | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| DEET |
|
|
| Picaridin |
|
|
| IR 3535 |
|
|
| Oil of Lemon Eucalyptus (PMD) |
|
|
| BioUD |
|
|
| Metofluthrin (Off! Clip-on Mosquito) |
|
|
Dengue
| How is Dengue transmitted? | When it is mostly spread? | What activities are risky? | Dengue symptoms | Preventing Dengue | Dengue treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The mild form
The severe form
|
|
For the mild form
For the severe form
|
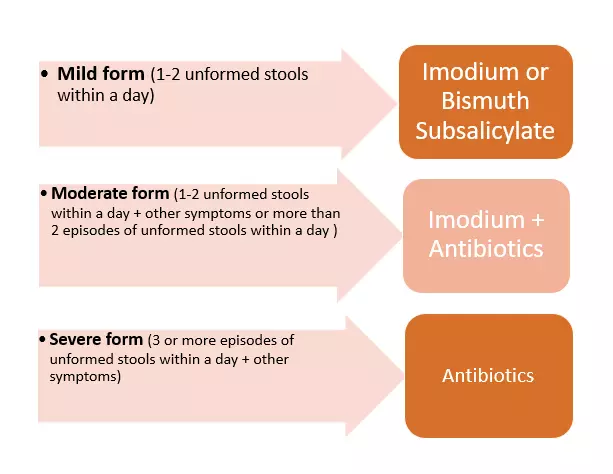
Travelers’ diarrhea
| The causes of the Travelers’ Diarrhea | Percentage of travelers with diarrhea in Southeast Asia Region | The prevention of Travelers’ Diarrhea |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Travelers’ diarrhea treatment